Today,
Spain is a democracy. Every four years there are elections to choose the government.
After
Juan Carlos became king in 1975, the
transition to democracy began. It ended in 1978 with a new constitution. Important reforms were introduced by the prime minister,
Adolfo Suarez.
.jpg) |
| By Verhoeff, Bert / Anefo (Nationaal Archief) [CC BY-SA 3.0 nl (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/nl/deed.en)], via Wikimedia Commons |
- All political parties were made legal.
- there was a democratic election in 1977.
- A new costitution was written.
 |
| By Infinauta (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons |
In 1978 people voted in favor of the constitution in a referendum. It established that:
Citizens have rights and responsibilities. Everyone must obey the law.
Citizens vote for their representatives freely in elections.
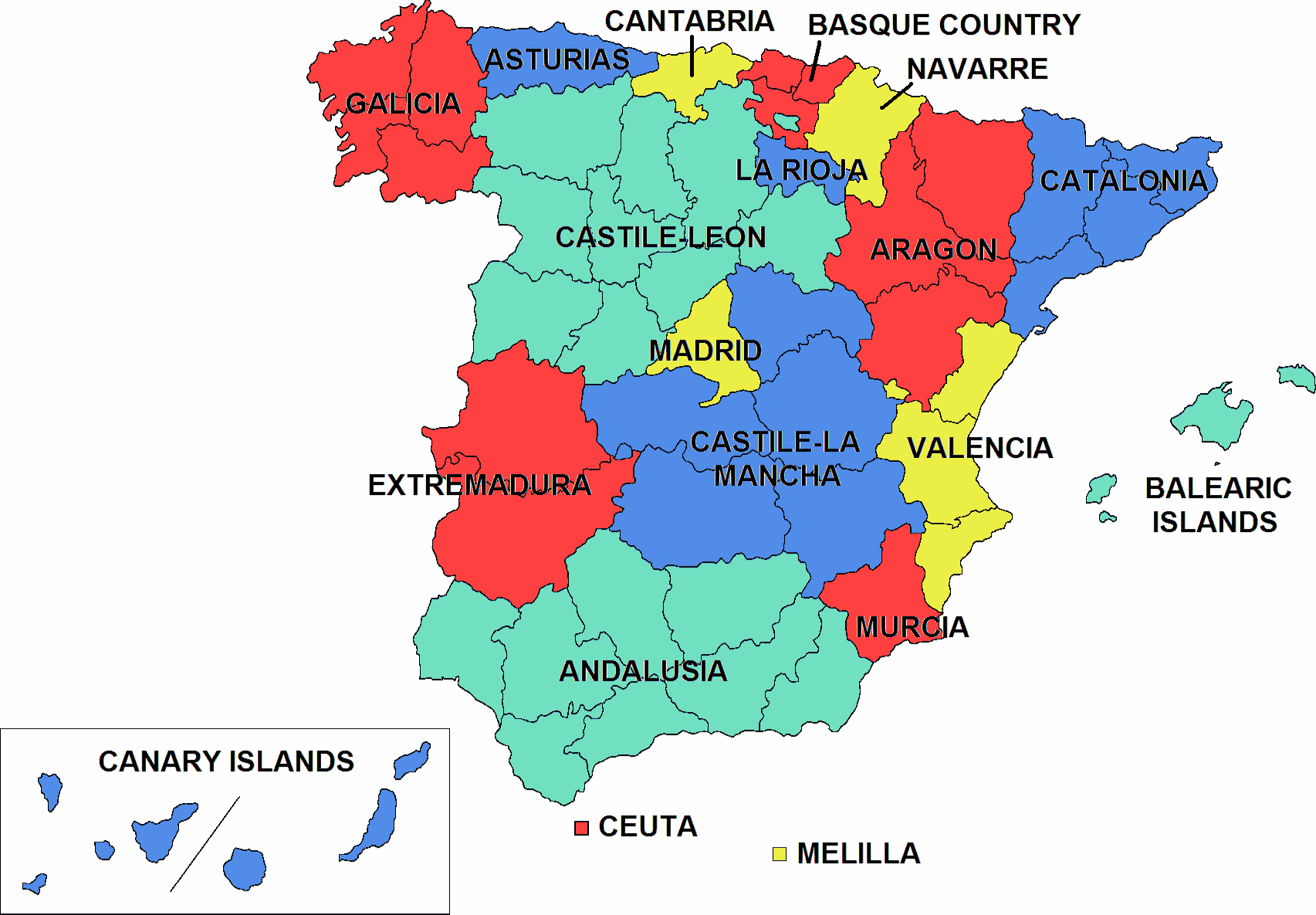
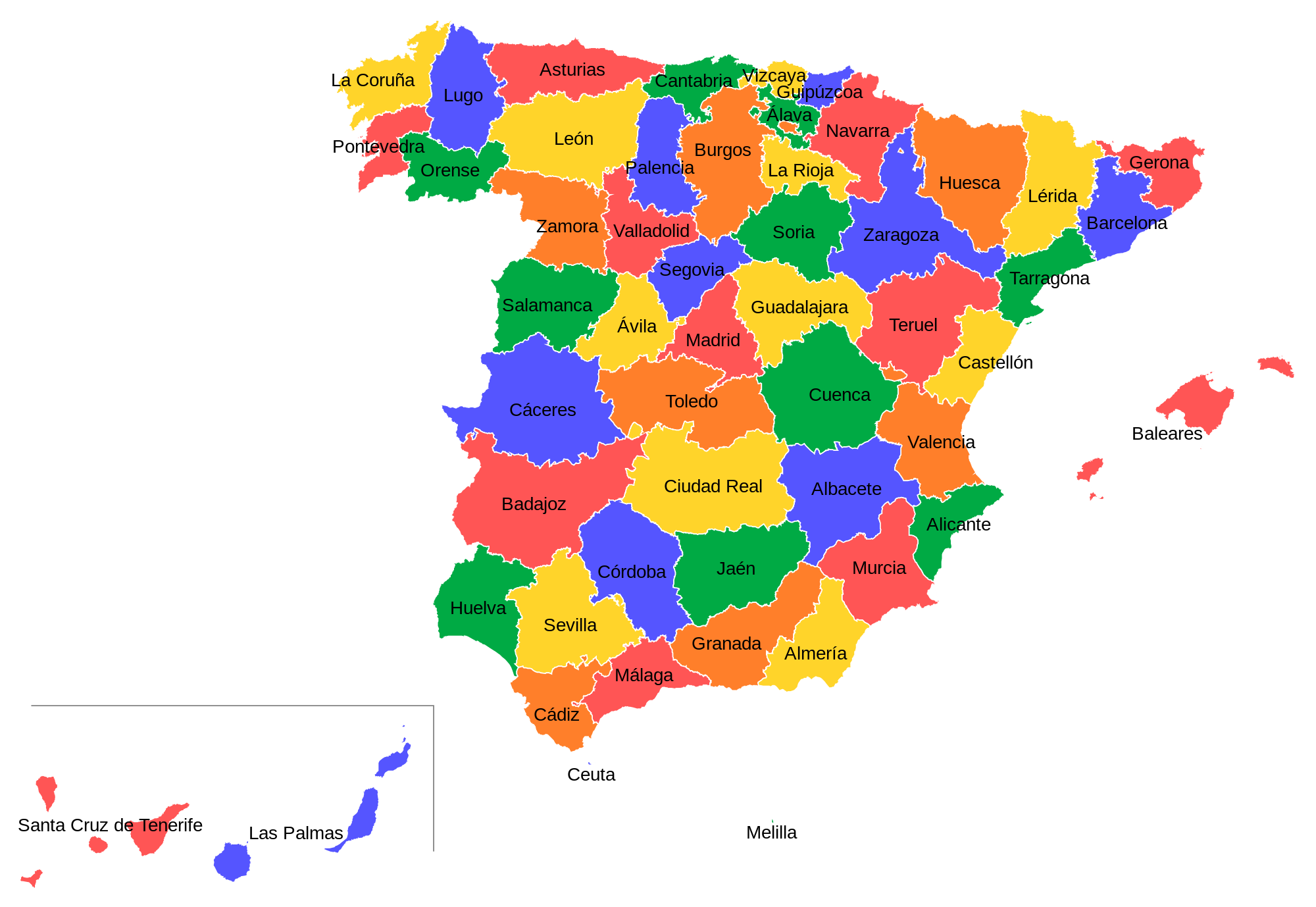
Spain recognises regional autonomy.
Spain is a parliamentary monarchy. The monarch is head of state but doesn´t govern or make laws.
Government is separated into three branches: the legislative, executive and judicial branches.
Since the transition two parties have governed Spain most of the time: the Socialist party (PSOE) and the Popular party (PP).
In 1981 there was an attemp military coup against the government led by Tejero. It failled.
In 1986 Spain became a member of the EEC (now UE).
 |
| By MPD01605 [CC BY-SA 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
In 1992 the euro replaced the peseta as Spain´s currency.
 |
| By Iu96 (Own work) [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
| By Avij (talk · contribs) (Own work) [ECB decisions ECB/2003/4 and ECB/2003/5 or Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons</a> |

_14.jpg)




















.jpg)







.jpg)

.jpg)


